Fact Files
Ultra-Processed Foods: How To Save Your Kids From 10 Potential Health Risks!
Unlocking Insights: Understanding Food Processing, Techniques, Categories, and Promoting Healthier Eating for Kids’ Well-being
After reading this article in the newspaper recently, I found myself contemplating and becoming concerned about my own eating habits. These concerns grew even more pronounced as I started considering the potential impact on my child, as well as all the members of my family. My apprehension expanded further when I contemplated the broader implications for society as a whole.
I must admit that I’m an enthusiastic fan of chips, regardless of whether they’re made from potatoes, tapioca, or anything else. It’s the texture, flavor, crispness, and taste that I crave. Once I start, I find it hard to stop eating chips, often devouring an entire 250-gram bag in one go. Popcorn with a spicy and crispy kick is yet another weakness of mine; I can’t resist until I’ve emptied a large bucket.
While I’m not particularly drawn to any other types of ultra-processed foods, chips seem to have an enduring hold on me. That last finger-licking moment is so precious that sometimes I even have to hide and discreetly enjoy licking my fingers after completing a bag of chips or a bucket of popcorn.
For some reason, I never seem to get attracted to fruits and vegetables. However, as I mature, I’m making an effort to train and refine my taste buds.
As I work on refining my habits, I’ve come to realize the importance of discussing, discovering, and adopting a healthier food style. In today’s fast-paced world, the appeal of ultra-processed foods has become overwhelming for many households. Nevertheless, it’s crucial to recognize that these foods pose substantial health risks, particularly for children.
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of food processing, various processing techniques, categories of food processing, the pros and cons, and offer guidelines for selecting wholesome and nutritious foods to support a natural and healthier lifestyle. We will also delve into the definition of ultra-processed foods, unveil the factors contributing to their addictive nature, and examine how parents can play a pivotal role in educating and steering their children towards healthier eating practices to ensure their well-being.
I agree that this article will be exceptionally comprehensive and extensive. It has the potential to be an eye-opener and may even lead some to make significant changes in their eating habits, shifting towards healthier options. So, I recommend taking the time to read it until the end!
What is food processing?
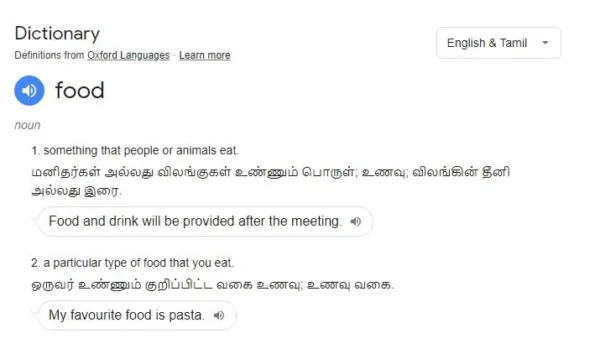
FOOD: something that people or animals eat.
Primitive humans, long ago, ate things they could find in the wild. They hunted animals like deer and boar for meat, caught fish in rivers and lakes, and gathered fruits, berries, nuts, and seeds. They also dug up roots and tubers for food and picked leafy greens and herbs. Their food was natural and not processed, and it helped them stay strong and healthy.
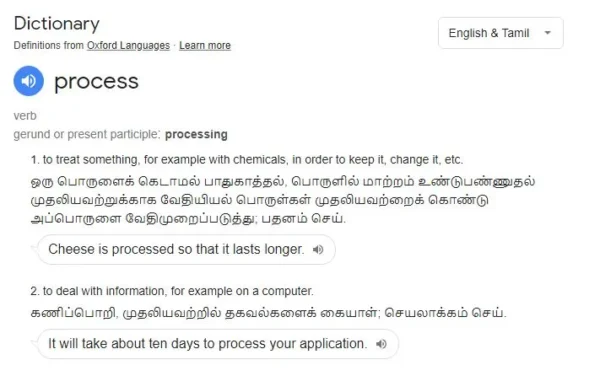
PROCESSING: The act or process of treating or preparing something by a special method. For example, the process wheat goes through before becoming a roti or a bread.
“Thousands of years ago, when humans first discovered cooking, they started processing food. After that came other basic methods like fermenting, drying, and preserving with salt. “
Food processing involves a range of methods and techniques used to transform raw ingredients into food products suitable for consumption. It plays a critical role in ensuring food safety, extending shelf life, and making food more convenient for consumers.
The purpose of food processing:
- Preservation: One of the primary purposes of food processing is to preserve food and prevent spoilage. Preservation methods include canning, freezing, drying, and pasteurization. These techniques help extend the shelf life of foods and reduce food waste.
- Enhancing Safety: Food processing often involves steps to reduce or eliminate harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria and pathogens. Techniques like pasteurization and sterilization kill or inactivate these microorganisms, making food safer to consume.
- Improving Convenience: Food processing can make food more convenient for consumers. Examples include pre-cut vegetables, instant meals, and ready-to-eat snacks, which save time and effort in meal preparation.
- Texture and Flavor Enhancement: Processing methods like baking, roasting, and frying can enhance the texture and flavor of foods, making them more appealing to consumers.
- Nutrient Retention: Some processing methods aim to retain the nutritional value of foods. For instance, freezing fruits and vegetables can help preserve their vitamins and minerals.
- Accessibility: Food processing can make certain foods accessible year-round, regardless of seasonal availability. Examples include canned fruits and vegetables.
Humans first learned to cook, and then to transform, preserve, and store foodstuffs safely.
The classification of food processing:
As per NOVA classification system of foods and food products, there are four groups of classification that categorize foods based on their degree of processing.
- Group 1 – Unprocessed or Minimally Processed Foods: These are foods that have undergone little to no processing and are very close to their natural state. Examples include fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and fresh meats and fish.
- Group 2 – Processed Culinary Ingredients: This group includes substances extracted from foods or nature and used in cooking to season and flavor dishes. Examples are salt, sugar, spices & masala powders, honey, and vegetable oils.
- Group 3 – Processed Foods: Processed foods have undergone moderate processing and often contain added substances like sugar, salt, or fats. Examples include pickles, canned vegetables, cheese, and bread.
- Group 4 – Ultra-Processed Food and Drink Products: These are highly processed foods and drinks that often contain numerous additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients. They are typically ready-to-eat or require minimal preparation. Examples include sugary cereals, soft drinks, fast food, and packaged snacks.
Now that we have a grasp of what food processing is and its classifications, let’s delve deep into the world of ultra-processed foods and the potential health risks associated with them.
What are Ultra-Processed Foods (UPF’s)?
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) represent a category of food products that have undergone extensive industrial processing, often characterized by the use of numerous additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients. These foods are typically highly processed, designed for long shelf life, and are often ready-to-eat or require minimal preparation. These foods typically have a low nutritional value and are high in calories, sugars, unhealthy fats, and salt. Ultra-processed foods are often highly palatable, convenient, and have a long shelf life, making them attractive to consumers. Ultra-processed foods are pervasive in modern diets and have garnered increasing attention from health experts and nutritionists due to their potential negative impacts on health.
Key Characteristics of Ultra-Processed Foods:
- Multiple Processing Steps: Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) go through several stages of processing, which can include milling, extrusion, molding, and various chemical treatments. These processes aim to transform raw ingredients into convenient and appealing final products.
- Additives and Preservatives: A hallmark of ultra-processed foods is the extensive use of food additives and preservatives. These may include artificial flavors, colors, emulsifiers, stabilizers, and sweeteners. These additives are often used to enhance taste, appearance, and shelf life.
- Minimal Whole Ingredients: UPFs tend to contain very few whole or minimally processed ingredients. Instead, they are composed mainly of refined components, such as sugars, unhealthy fats, and highly processed flours.
- Highly Palatable: Ultra-processed foods are engineered to be extremely palatable, often striking the perfect balance of saltiness, sweetness, and umami. This palatability can make these foods more appealing and difficult to resist.
Advantages of Ultra-Processed Foods:
- Convenience: Ultra-processed foods are easy to prepare and often require little to no cooking or preparation, which can save time and effort in meal preparation.
- Long Shelf Life: These foods tend to have a longer shelf life due to the use of preservatives and additives, reducing food waste.
- Availability: Ultra-processed foods are widely available and can be found in most supermarkets and convenience stores, making them accessible to many people.
Disadvantages and 10 Potential Health Risks of Ultra-Processed Foods:
Consuming too much ultra-processed food can have a range of negative health consequences due to their poor nutritional quality and high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, sodium, and artificial additives. Here are some potential health problems and risks associated with excessive consumption of ultra-processed foods:
- Weight Gain and Obesity: Ultra-processed foods are often calorie-dense but nutrient-poor, meaning they provide a lot of calories but few essential nutrients. Overconsumption of these foods can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity.
- Cardiovascular Disease: A diet high in ultra-processed foods has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. The high levels of unhealthy fats and sodium in these foods can contribute to high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excessive consumption of sugary ultra-processed foods can lead to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Processed foods often cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- High Blood Pressure: The high salt content in many ultra-processed foods can contribute to hypertension (high blood pressure), a risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Cancer: Some studies have suggested a link between a diet rich in ultra-processed foods and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as colorectal cancer.
- Digestive Problems: Ultra-processed foods are typically low in dietary fiber, which can lead to digestive issues such as constipation and an increased risk of gastrointestinal diseases.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Because these foods lack essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, relying heavily on ultra-processed foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies over time.
- Mental Health Issues: There is evidence to suggest that a diet high in ultra-processed foods may be associated with an increased risk of mental health problems, including depression and anxiety.
- Addiction and Overeating: The highly palatable nature of ultra-processed foods, combined with their addictive qualities (as discussed in a previous response), can lead to overeating and difficulties in controlling food intake.
- Dental Problems: Many ultra-processed foods, especially sugary snacks and beverages, can contribute to dental issues such as cavities and tooth decay.
How Sugar, Excess Calories & Ultra-Processed Foods Cause Obesity & Cancer | Dr. Robert Lustig
Four hours of video on the connection between sugar, excess calories, and ultra-processed foods causing obesity and cancer? Are you kidding? Trust me, while this video is just as extensive and comprehensive as this article, it delivers a wealth of information and insights straight from the medical professional, Dr. Robert Lustig. Hosted by Dhru Purohit, they’ve done an excellent job delving into this topic, a feat made possible only when you genuinely care about the well-being of humanity.
At Kurinzi Foodstyle, our approach aligns with the principles mentioned in the video, much like the Kuwaiti Danish Dairy (KDD). I strongly recommend watching this video until the end, perhaps in multiple sittings 🙂
The article ‘Food meets health: How a new approach to metabolic health could tackle chronic disease,’ written by Sir Mohammad Jaafar, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Kuwaiti Danish Dairy (KDD), discusses the Metabolic Matrix that Dr. Robert Lustig talks about in the video above.
Examples of Ultra-Processed Foods:
- Sugary Breakfast Cereals: Many breakfast cereals are loaded with added sugars, artificial flavors, and colors. They often lack essential nutrients and dietary fiber.
- Soda and Sugary Drinks: Soft drinks like cola, lemon-lime sodas, and fruit-flavored beverages are prime examples of ultra-processed drinks. They contain excessive amounts of sugar and little to no nutritional value.
- Fast Food Items: Burgers, fries, chicken nuggets, and other fast food items are highly processed, with ingredients like processed meats, deep-fried potatoes, and sugary condiments.
- Packaged Snacks: Chips, crackers, cookies, and candy are classic examples of ultra-processed snacks. They are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and artificial additives.
- Frozen Pizza: Commercial frozen pizzas typically contain processed meats, refined flours, and heavily processed cheese, often accompanied by artificial flavors and preservatives.
- Instant Noodles: Instant ramen noodles and similar products are ultra-processed due to their extensive processing and addition of synthetic flavorings and preservatives.
- Processed Meats: Hot dogs, sausages, bacon, and deli meats are highly processed and often contain additives, preservatives, and unhealthy fats.
- Store-Bought Baked Goods: Cakes, pastries, muffins, and other store-bought baked goods are made with refined flours, added sugars, and artificial flavorings.
- Sugary and Flavored Yogurts: Many flavored yogurts contain high amounts of added sugars and artificial flavors, negating the potential health benefits of yogurt.
- Microwaveable Meals: Frozen microwaveable meals like TV dinners often contain highly processed ingredients, excessive salt, and unhealthy fats.
- Sweetened Breakfast Bars: Breakfast bars marketed as healthy options can be ultra-processed, packed with sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients.
- Processed Soups: Canned and instant soups often contain high levels of sodium, artificial flavors, and preservatives.
- Sauces and Condiments: Some sauces like ketchup, barbecue sauce, and salad dressings are laden with added sugars, salt, and artificial additives.
- Sugary Breakfast Pastries: Pastries like doughnuts and sweet rolls are typically high in sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Flavored and Sweetened Beverages: Aside from soda, other beverages like fruit juices, energy drinks, and sweetened iced teas often contain excessive added sugars.
- Processed Cheese Products: Cheese spreads, cheese-flavored snacks, and processed cheese slices undergo extensive processing and often contain additives.
- Sugary Desserts: Commercially produced cakes, pies, and desserts are usually high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial ingredients.
- Instant Potatoes and Rice Mixes: These convenience foods are processed and often contain additives to enhance flavor and texture.
- Canned Fruit in Syrup: Canned fruits preserved in heavy syrup have added sugars that reduce their nutritional value.
- Flavored Instant Oatmeal: Prepackaged flavored oatmeal can contain high amounts of added sugars and artificial flavorings.
😮 So, does this mean we should almost completely eliminate ready-to-eat options from our diet?
Not really! 🤔
Why are Ultra-Processed Foods Addictive?
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) are often considered addictive because
- High Sugar Content: One of the primary reasons for the addictive nature of UPFs is their high sugar content. Many ultra-processed products, such as sugary cereals, sweet snacks, and soft drinks, contain excessive amounts of added sugars. Sugar triggers the brain’s reward system, leading to the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reinforcement. This pleasurable response creates a craving for more sugary foods, contributing to addictive eating patterns.
- Unhealthy Fats: Ultra-processed foods are often laden with unhealthy fats, particularly trans fats and saturated fats. These fats can enhance the palatability and texture of foods, making them more appealing. The combination of sugar and unhealthy fats can create a powerful “bliss point” that keeps people coming back for more.
- Sodium (Salt) Content: High salt levels are another common feature of UPFs. Salt can enhance the flavors of processed foods, making them more satisfying and stimulating the taste buds. Excess salt intake can lead to cravings for salty foods, contributing to overconsumption.
- Artificial Flavor Enhancers: Many ultra-processed foods contain artificial flavor enhancers like monosodium glutamate (MSG). You might be familiar with Ajinomoto, a brand name for monosodium glutamate (MSG), a common food additive used to enhance the flavor of dishes. These substances work to intensify the taste and aroma of foods, making them exceptionally enticing. The umami sensation produced by MSG can be particularly captivating, further stimulating the desire to consume these products.
- Texture and Mouthfeel: The texture and mouthfeel of UPFs are often carefully engineered to provide a pleasant eating experience. Crispy chips, creamy ice cream, and crunchy cookies create sensory satisfaction that can lead to cravings and overeating.
- Hyper-Palatability: Ultra-processed foods are intentionally formulated to be hyper-palatable, striking the perfect balance of sweetness, saltiness, and savory flavors. This hyper-palatability can hijack the brain’s reward system, making these foods irresistible and difficult to resist.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Ultra-processed foods are readily available, convenient, and require minimal preparation. Their ubiquity and ease of access can lead to frequent consumption, reinforcing addictive eating habits.
- Marketing and Advertising: Aggressive marketing and advertising campaigns by food companies create strong brand associations and emotional connections with UPFs. These associations can lead to cravings and a sense of comfort associated with consuming these products.
- Psychological Factors: The convenience, affordability, and sensory appeal of UPFs can provide a quick and easy solution to stress, boredom, or emotional distress. This emotional connection can contribute to addictive eating behaviors, as individuals turn to these foods as a form of comfort or stress relief.
- Tolerance and Withdrawal: Over time, regular consumption of ultra-processed foods can lead to tolerance, where individuals require more of these foods to experience the same level of pleasure. When people attempt to reduce their consumption, they may experience withdrawal symptoms, including cravings, irritability, and mood swings, reinforcing their dependence on these foods.
The addictive nature of ultra-processed foods can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the high levels of sugar, unhealthy fats, salt, artificial additives, and the deliberate engineering of taste, texture, and convenience. Recognizing the addictive potential of UPFs is crucial for making informed dietary choices and promoting healthier eating habits.
Difference Between Home Cooked vs. Ultra-Processed Foods and How to Choose the Right Food Habits
Home-Cooked Meals:
- Ingredients: Home-cooked meals typically use whole, unprocessed or minimally processed ingredients. These include fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Control Over Ingredients: When cooking at home, you have full control over the quality and quantity of ingredients. You can select organic or locally sourced ingredients, which can be beneficial for health and the environment.
- Nutritional Value: Home-cooked meals are often more nutritious, as they retain their natural vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. They offer a balanced mix of nutrients necessary for optimal health.
- Customization: You can tailor home-cooked meals to meet specific dietary preferences and restrictions, such as vegetarian, gluten-free, or low-sodium diets.
- Cooking Methods: You can choose healthier cooking methods, such as steaming, grilling, roasting, or sautéing, which retain the nutritional value of foods.
- Portion Control: Portion sizes can be controlled more effectively at home, reducing the risk of overeating.
- Less Sodium: Home-cooked meals tend to have lower sodium content compared to their processed counterparts, promoting heart health.
Ultra-Processed Foods:
- Ingredients: Ultra-processed foods are made from highly processed and refined ingredients. They often contain additives, preservatives, artificial flavorings, and unhealthy fats.
- Limited Control: Consumers have minimal control over the quality and quantity of ingredients in ultra-processed foods, as they are pre-packaged and ready-to-eat.
- Nutritional Value: Ultra-processed foods are typically low in essential nutrients and high in empty calories, added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. They provide little nutritional benefit.
- Limited Customization: These foods are mass-produced and not easily customizable to individual dietary needs or preferences.
- Processing Methods: Ultra-processed foods undergo extensive industrial processing, which can lead to the loss of natural nutrients and the addition of harmful substances.
- Large Portions: Packaging often encourages larger portion sizes, contributing to overconsumption.
- High Sodium: Ultra-processed foods often contain excessive amounts of salt, which can lead to hypertension and other health issues.
Choosing the Right Food Habits:
- Prioritize Whole Foods: Incorporate more whole, unprocessed or minimally processed foods into your diet. These include fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
- Cook at Home: Make an effort to cook meals at home as often as possible. This gives you control over the ingredients and cooking methods.
- Read Labels: When purchasing packaged foods, read ingredient labels carefully. Choose products with shorter ingredient lists, and avoid those with artificial additives or excessive sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats.
- Reduce Ultra-Processed Foods: Gradually reduce the consumption of ultra-processed foods in your diet. Replace them with healthier alternatives, such as homemade snacks or whole-food options.
- Plan Meals: Plan your meals ahead of time to ensure you have nutritious options available. This reduces the temptation to turn to convenience foods.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the nutritional content of the foods you consume. Understand how specific ingredients and processing methods can impact your health.
- Cooking Skills: Invest in developing basic cooking skills if you’re not already proficient in the kitchen. Cooking can be a rewarding and enjoyable activity.
- Family Involvement: Involve your family, including children, in meal planning and preparation. Educate them about the benefits of healthier food choices.
- Moderation: While ultra-processed foods should be limited, occasional indulgence is okay. The key is moderation and balance in your overall diet.
- Consult Professionals: If you have specific dietary concerns or health conditions, consider seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist who can tailor recommendations to your needs.
The choice between home-cooked meals and ultra-processed foods can significantly impact your health. Prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods and cooking at home empowers you to make healthier food choices and develop sustainable food habits that support long-term well-being. Remember that small, gradual changes in your diet can lead to significant improvements in your health over time.

How to Help Kids Avoid Ultra-Processed Foods and Nurture Healthy Eating Habits
Helping kids avoid ultra-processed foods and nurturing healthy eating habits is essential for their overall well-being. Here’s a detailed guide on how we, as parents can achieve this:
- Be a Role Model: Children learn by example, so one of the most effective ways to instill healthy eating habits in them is to model those habits yourself. When children see parents making nutritious food choices, they are more likely to follow suit.
Education and Explanation: Teach children about the difference between whole, natural foods and ultra-processed ones. Use age-appropriate language and examples to help them understand.
Explain why certain foods are healthier than others, emphasizing the benefits of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Discuss the potential health risks associated with excessive consumption of ultra-processed foods in a simple and age-appropriate manner.
Involve Kids in Meal Planning and Preparation: Engage children in the process of planning and preparing meals. This not only gives them a sense of ownership but also teaches them valuable cooking skills.
Let them choose fruits and vegetables at the grocery store or farmers’ market, and involve them in washing, chopping, and cooking.
Create a family cookbook or a recipe box with their favorite healthy recipes.
- Keep Healthy Foods Accessible: Stock your kitchen with whole, unprocessed foods. Have plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins readily available.
Make healthy snacks easily accessible in the pantry and fridge. Cut up fruits and veggies for quick and convenient options.
Limit the presence of ultra-processed foods at home to reduce temptation.
- Limit Exposure to Junk Food Marketing:
Be mindful of the media your children are exposed to. Junk food advertising can influence their preferences.
Encourage critical thinking by discussing how advertisements aim to make foods seem more appealing than they actually are.
- Set Regular Meal and Snack Times:
Establish a routine for meal and snack times. Consistency helps regulate hunger and reduces the likelihood of impulse snacking on unhealthy options.
Offer a variety of nutrient-rich foods during meals to ensure balanced nutrition.
- Encourage Exploration and Variety: Encourage kids to try new foods and explore different flavors and textures. Make trying new foods a positive and fun experience.
Rotate foods to provide variety in their diet and avoid food fatigue.
- Monitor Portion Sizes: Teach children about appropriate portion sizes to help them recognize when they are full and prevent overeating.
Avoid using food as a reward or punishment, as this can create unhealthy emotional associations with eating.
- Be Patient and Positive: Understand that developing healthy eating habits is a gradual process. Be patient with children as they adapt to new foods and preferences.
Praise and reinforce positive eating behaviors. Avoid using negative language or pressure when it comes to food.
- Encourage Physical Activity: Promote an active lifestyle by engaging in physical activities as a family. Active kids are more likely to make healthier food choices.
Emphasize the importance of exercise for overall health and well-being.
- Gradual Reduction of Ultra-Processed Foods: Start by gradually reducing the presence of ultra-processed foods in your child’s diet rather than eliminating them abruptly. Sudden changes can lead to resistance.
Replace unhealthy snacks with healthier alternatives. For example, switch from sugary cereals to whole-grain options or replace soda with water or naturally flavored beverages.
- Celebrate Special Occasions Mindfully: On special occasions or celebrations, allow for treats in moderation. Teach kids that it’s okay to enjoy indulgent foods occasionally but not as an everyday habit.
- Be Supportive: Encourage open communication about food and nutrition. Address any questions or concerns your child may have without judgment.
Seek the advice of a pediatrician or registered dietitian if you have specific concerns about your child’s diet or eating habits.
By implementing these strategies and fostering a positive food environment at home, parents can help children develop healthy eating habits that will benefit them throughout their lives. Remember that creating a supportive and nurturing atmosphere around food is key to success.

Which category of the NOVA classification system does Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO) belong to?
Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO) typically falls under Group 2 of the NOVA classification system. Group 2 includes processed culinary ingredients like oils and fats that are used in cooking to season and flavor dishes. VCO is derived from coconuts through a mechanical extraction process, which doesn’t involve significant chemical or industrial processing. It is primarily used as a cooking oil and a flavoring agent, making it a processed culinary ingredient.
Is Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO) considered an Ultra-Processed Food?
No, Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO) is not an ultra-processed food. Kurinzi VCO is derived from dried copras of handpicked coconuts harvested from naturally manured tall trees, and the oil is extracted using traditional cold-wood pressing methods. It is a minimally processed oil that retains many of the coconut’s natural flavor, aroma, and nutritional benefits.
Why VCO is the Best Choice While Cooking at Home Compared to Ultra-Processed Food:
Minimal Processing: VCO is produced through simple mechanical processes that do not involve extensive industrial processing, chemical treatments, or the addition of artificial additives. This minimal processing helps preserve its natural properties.
Nutrient Retention: VCO retains the natural nutrients found in coconuts, including vitamins, minerals, and medium-chain fatty acids like lauric acid. These nutrients can provide various health benefits, including immune support and improved digestion.
High Smoke Point: VCO has a high smoke point (around 350°F or 177°C), which makes it suitable for various cooking methods, including frying, sautéing, and roasting. Its stability at high temperatures means it does not easily break down and produce harmful compounds.
Natural Flavor and Aroma: VCO has a pleasant, mild coconut flavor and aroma that can enhance the taste of dishes. It can be used in both sweet and savory recipes to add a subtle coconut essence.
Versatility: VCO is a versatile cooking oil that can be used for a wide range of culinary applications, from stir-frying vegetables to baking and making salad dressings. Its versatility makes it a valuable addition to your kitchen.
Health Benefits: VCO has been associated with various health benefits, including improved heart health, increased HDL (good) cholesterol, and potential antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It is also considered a source of healthy saturated fats.
Alternative to Hydrogenated Oils: VCO can be an excellent substitute for hydrogenated oils and trans fats, which are commonly found in many ultra-processed foods. These unhealthy fats have been linked to various health problems, including heart disease.
Control Over Quality: When purchasing VCO, you have the option to choose high-quality, organic, and unrefined varieties. This allows you to ensure that the product you use is of the highest quality.
No Artificial Additives: VCO is a natural product that does not contain artificial additives, preservatives, or harmful chemicals often found in ultra-processed foods.
Promotes Whole Food Cooking: Choosing VCO encourages the use of whole and minimally processed ingredients in your recipes, promoting a healthier and more balanced diet.
In summary, Virgin Coconut Oil is not an ultra-processed food; it is a minimally processed and natural cooking oil that offers several health benefits and culinary advantages. When compared to ultra-processed cooking oils and fats, VCO stands out as a healthier and more wholesome choice for cooking at home. It can enhance the flavor of your dishes while contributing to a nutritious and balanced diet.
REFERENCES:
SCIENCEDIRECT – Ultraprocessed Foods and Obesity Risk: A Critical Review of Reported Mechanisms
HEALTHLINE: Eating ‘Ultra-Processed’ Foods Can Shave Years Off Your Life
NOVA – The food classification system
International Food Information Council Foundation (IFIC)
National Library of Medicine – The Effects of Ultra-Processed Food Consumption—Is There Any Action Needed?
Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
For every perspective, there is invariably an opposing and contradictory viewpoint. In this instance, we encountered a critical perspective on the NOVA classification system titled “The NOVA classification system: A critical perspective in food science.” This alternative viewpoint is certainly worth exploring.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
PUBLISHED ON – V1:/ 22-10-23
UPDATED ON – V1:/ 22-10-23
Posted on: Instagram | Facebook | Twitter | Pinterest | Threads
You May Be Also Interested in
Have you ever tried cooking with Virgin Coconut Oil?
Crucial Insights on Trans Fats:Exploring Sources, Health Risks, and the Nutritional Edge of Kurinzi’s Virgin Coconut Oil

















This article is incredibly well-researched, especially in regard to foods. As a parent, I found a strong connection with all the points discussed. It has made me more aware of my food choices, and I genuinely appreciate the in-depth insights provided in the article. Thank you for this enlightening read!
Thank you for your kind words and for taking the time to read our article. We’re delighted to hear that you found it insightful and that it resonated with you as a parent. Making informed food choices is crucial for our well-being, and we’re glad we could contribute to your awareness. Your appreciation motivates us to continue providing valuable information. Thanks for being a part of our community!
I greatly appreciate this extensively studied article on ultra-processed food. It breaks down the topic from the simplest understanding of “food” to the complex details of various processing methods, providing clear explanations and relatable examples at each level of processing.
The article’s comprehensive approach sheds light on the extent of ultra-processed foods in our daily diets. It contradicts common man assumptions that such foods are limited to canned products, vegetables, or meats that might not be consumed regularly in our country. The long list of ultra-processed foods we commonly consume serves as an eye-opener, highlighting that this issue isn’t confined to foreign lands or a small segment of the population in our country. It emphasizes the importance of awareness and informed choices regarding our daily food intake. Thank you!!
Thank you for your kind words and for taking the time to read our article. We’re delighted to hear that you found it insightful and that it resonated with you as a parent. Making informed food choices is crucial for our well-being, and we’re glad we could contribute to your awareness. Your appreciation motivates us to continue providing valuable information. Thanks for being a part of our community!